Constraining Pattern-Copied Objects
This section refers to objects copied in patterns (lines, linear arrays, radial arrays), using the Copy Entities tools . When you copy objects in a pattern, you can use Auto Constraints and dimension variables to control spacing, angles, etc. This example uses a circle copied into a linear array.
-
Before you begin, make sure Auto Add Constraints is active in the Inspector Bar.
-
Create a rectangle and add a small circle. The rectangle should have parallel and coincident constraints assigned automatically.
-
Select the circle and use Fit Array Copy to copy the circle into a grid.
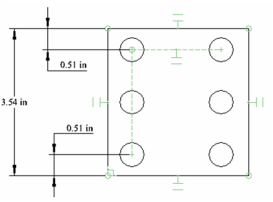
- Assign some Orthogonal dimensions as shown.
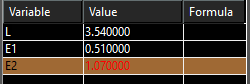
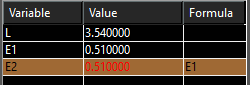
- Open the Variables palette (F2) and the dimensions should be shown, identified by a variable. In this example, the variables were assigned names (L, E1, E2).
Note: For more information on working with variables,
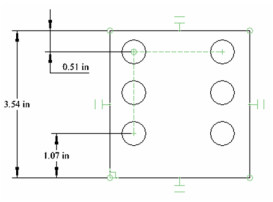
- Create a formula so that the two edge dimensions will be equal. In this case, the variable E1 was used as the formula for E2.
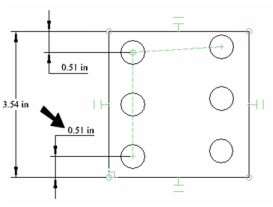
The dimensions update, and the spacing between copied objects remains constant. However, in this case, the linear array does not have a 90 degree angle.
-
Used the Horizontal constraint on the bottom edge of the rectangle.
-
To fix this, activate the Parallel constraint and click first the array (horizontal) constraint line, then the top line of the rectangle. Repeat if necessary to make the array perpendicular vertically.
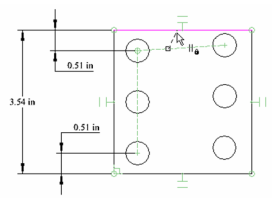
Now the array is perpendicular again.